To understand what DeFi 2.0 is, we must take into account the words of Napoleon Bonaparte: "No battle plan survives the enemy's first shot." DeFi 2.0 is not an innovation that breaks with previous versions, but rather learning from the limitations of the previous version points to a more professional use
All technology needs time to mature in the market to be available for general use and all innovations based on the use of the blockchain are no exception. As Moore's well-known scheme points out, before becoming massive, any technology is adopted by a small number of innovators, then spread to a slightly larger number of early users, before being used by a majority.
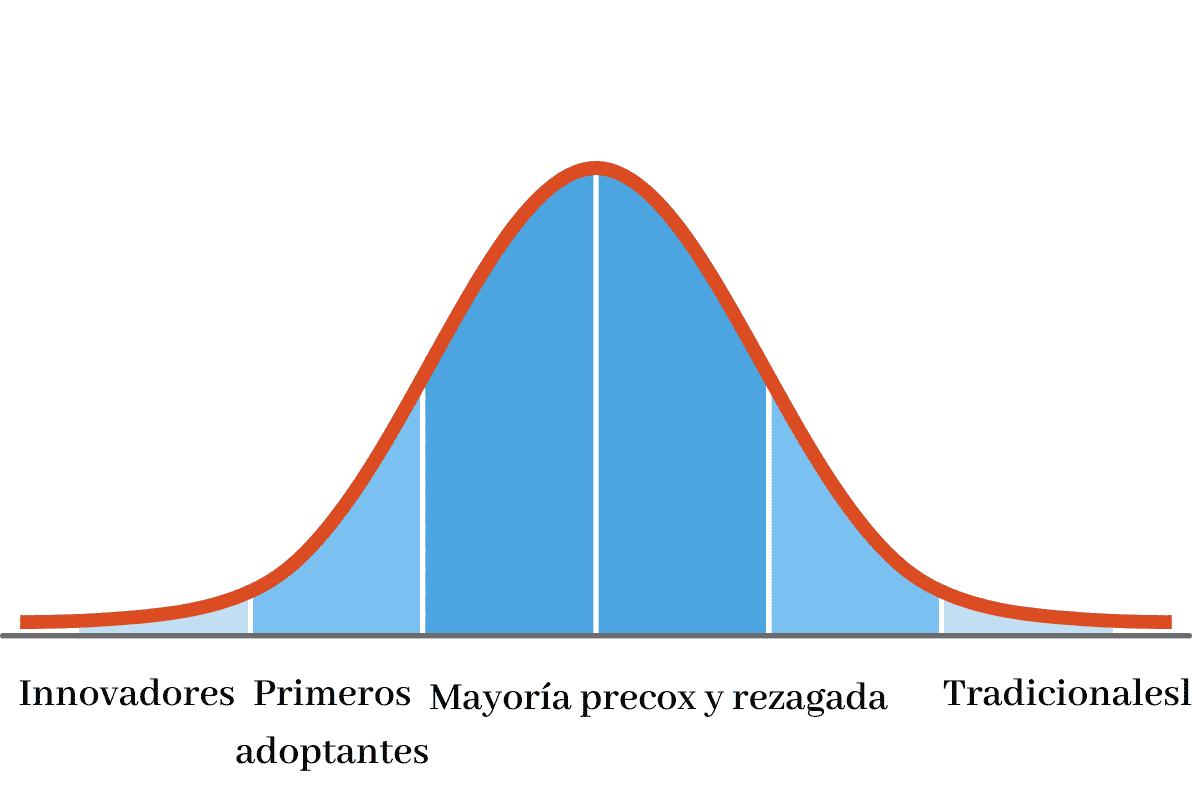
Of course, not all innovations make it past the early adopter stage. Many are unable to adapt to the challenges of real-life use. Defi 2.0 is, then, the attempt by the developers of blockchain-based financial decentralization services to develop products that are used by a majority based on the feedback obtained from their use by innovators and early users.
The limitations of DeFi 1.0
In the two years that decentralized financial services have been with us, they have achieved significant success among innovators and early users. It was that success, which revealed the shortcomings that prevent its use on a massive scale.
These are some of the problems:
- More demand than supply: The platforms that popular projects are based on seem unable to process transactions at a reasonable speed due to the number of users. To this we must add that the costs for the service are usually high.
- Insufficient sources of information reliable on external issues.
- centralization it is still very high. despite the name.
- Insufficient internal control: Although security audits are performed, they are not done frequently enough to keep pace with updates.
- management : There is not enough capital for all DeFi-based projects.
What is DeFi 2.0
Under the umbrella of this name we find uA series of projects focused on solving the above mentioned problems. The objectives of all these projects are:
- Facilitate interaction between users either within the same project or with those of similar projects.
- Improved decision-making process and policy determination through the democratic participation of community members behind each project.
- Easier incentive schemes to understand and participate as a way to get new users or that the current ones get more involved.
- Greater ease of use: A recurring complaint from DeFi 1.0 users is the complexity of the user interface. 2.0 services are focused on facilitating their use.
- Greater protection against breaches of smart contracts by offering insurance.
- Compensation for losses caused by the change in the price relationship between two cryptocurrencies.
- Self-paying loans: The lender retains a small percentage of the total loan amount and invests it for profit. Those profits go toward paying off the loan. Once the payment is complete, the amount withheld is sent to the loan applicant.
Some services based on DeFi 2.0

Initiatives based on DeFi 2.0 improve existing services and incorporate others: Let's see some examples:
- Guarantees for yield agriculture: Yield farming consists of making investments in the cryptocurrency market using third-party funds in exchange for the profits made. DeFi 2.0 services allow operators to use tokens as collateral for repayment of loans.
- Staking: This is a way to generate income simply by being part of the blockchain network behind each service. In this way, it contributes to the backup of the records of the operations.
- Loans: I already explained above the mechanism of self-paying loans, which makes them more accessible than traditional loans.
- Hassle-Free Investment Opportunities: Liquidity funds allow any user to participate in the cryptocurrency exchange market and obtain profits without having too much knowledge.
Risks of DeFi 2.0
It would be irresponsible of me to suggest that DeFi 2.0 is without problems and risks. Let's see some
- Vulnerabilities of computer systems: It is inevitable that in millions of lines of code there will be errors. Also, the more massive a platform becomes, computer criminals appear determined to find and take advantage of them.
- Future regulations: Politicians will always be politicians. In other words, they will always be looking for new services to tax and new activities to regulate. As decentralized financial services become massive, taxes and regulations will appear.
- Volatility: Decentralized financial services may be virtual, but their users are in the real world. Any turbulence in the economy will affect the value of digital assets and the availability of liquidity.









